Even the most beautiful teeth are not attractive if they are not framed with healthy and properly shaped gums. Non-aesthetic gums can be corrected with treatments and minor operations on your gums.
- Unhealthy gums,
- Smile with gums (Gummy Smile; cases where the gums are more visible when they smile)
- Gingival recession,
- Irregular gingival edges,
- Gingival pigmentation.
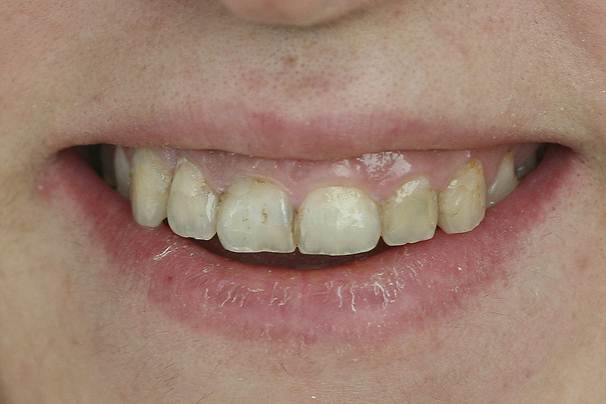
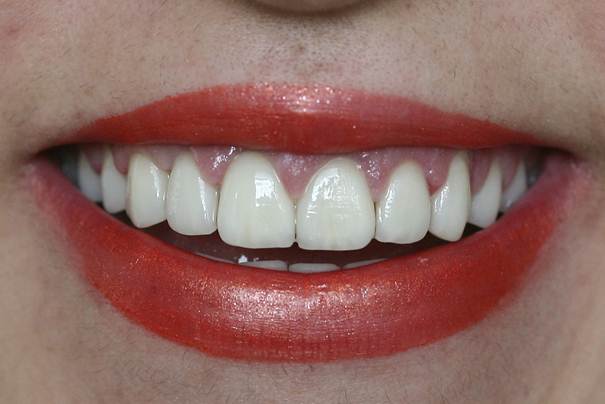
Gingivectomy and Gingivoplasty
Gingivectomy is the surgical removal of gingival tissue. Gingivoplasty is the shaping of healthy gingival tissues around the tooth.
Gingivectomy is a treatment developed for the treatment of gum disease. Today it is also used for aesthetic arrangements.
There are two reasons for gingival tissue removal. The first reason is the presence of gingival pockets formed between the tooth and the gums. With the accumulation of food residues and bacterial colonies in these areas, cleaning difficulties arise. If these pockets contain gingival tissue only, they can be removed by gingivectomy.
In some cases, there may be a large amount of gums around the tooth. This prevents the teeth and gums from being kept clean. It is also a cosmetic problem. In severe cases, it may be sized to affect chewing and speech. As with epilepsy drugs, some medications can cause excessive gingival enlargement. Sometimes there may be no obvious reason.
The gums that are reshaped with the help of gingivoplasty have a more natural appearance. Disfigured or asymmetrical gums can be corrected with this procedure due to genetics, disease or trauma.
This process can also be done only due to cosmetic needs. Gingivoplasty is usually performed alone. However, in some cases, it can be applied after gingivectomy or graft application at the gingival border.
Before removing gingivectomy and gingivoplasty, dental calculus cleaning and root surface flattening may be required to remove dental calculus from existing gingival pockets. Gingivectomy and gingivoplasties are usually done with hand tools. But it can also be done with electrosurgical instruments, laser and / or rotary instruments.
- Local anesthesia is performed to numb the gums.
- During the healing period, the mouth should be kept clean.
Flap Operation
If periodontal pockets cannot be shallow by curettage and straightening the root surface, the gingiva that forms the pocket is surgically removed.
The purpose of gingival flap surgery is to treat gum disease (periodontitis). This procedure is recommended for people with moderate or advanced gum disease. If gingival infection cannot be eliminated with a non-surgical method, gingival flap surgery is used. Gingival flap surgery can also be performed in conjunction with another procedure, bone surgery.
The region is primarily anesthetized with local anesthesia. The gums are separated from the teeth with the help of a hand tool. Thus, the periodontist can directly access the roots and the bone tissue supporting the tooth. Infected tissues are then removed between the teeth and holes (defects) in the bone. dental cleaning and root surface smoothing are applied. If there are defects in the bone, they can be reshaped by reshaping. During this process, bone corners can be softened using Er: YAG laser or rotary tools.
After these procedures, the gums are placed back on the teeth and fixed with stitches.
It is very important to keep this area as clean as possible while the surgical area is healing. You should continue brushing your teeth and using dental floss in the remaining areas.
If the periodontal bandage was used to protect the surgical area, it should be ensured that the plaque is removed gently from the teeth. Antimicrobial mouthwashes with chlorhexidine are usually prescribed after periodontal surgery. These mouthwashes do not remove the plaque, but it helps kill the bacteria and heal the mouth.
Crown Length Extension Operation
It is a simple procedure to lengthen the parts of the teeth (visible in the mouth) above the level of the gums.
In periodontal surgical interventions, soft tissue lasers are used successfully as well as classical surgical methods and effective results are obtained.
Tissue Grafts
Soft Tissue Grafts: It is the process of covering the apparent gingival recessions occurring in one or more teeth due to anatomical errors or gum diseases with soft tissue pieces taken from a different part of the mouth (usually palate).
Hard Tissue Grafts: During flap operations, bone making is stimulated by artificial or natural bone bone applications in areas where bone loss is advanced.

